Fatty Liver Disease: In recent years, fatty liver disease has emerged as a significant health concern, affecting individuals globally. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the complexities of fatty liver disease, providing an in-depth understanding of its causes, symptoms, risk factors, and actionable steps to take toward health. As we proceed on this exploration, we will uncover the complexities of this condition and empower readers with the knowledge needed for effective prevention and management.
Table of Contents
Demystifying Fatty Liver Disease
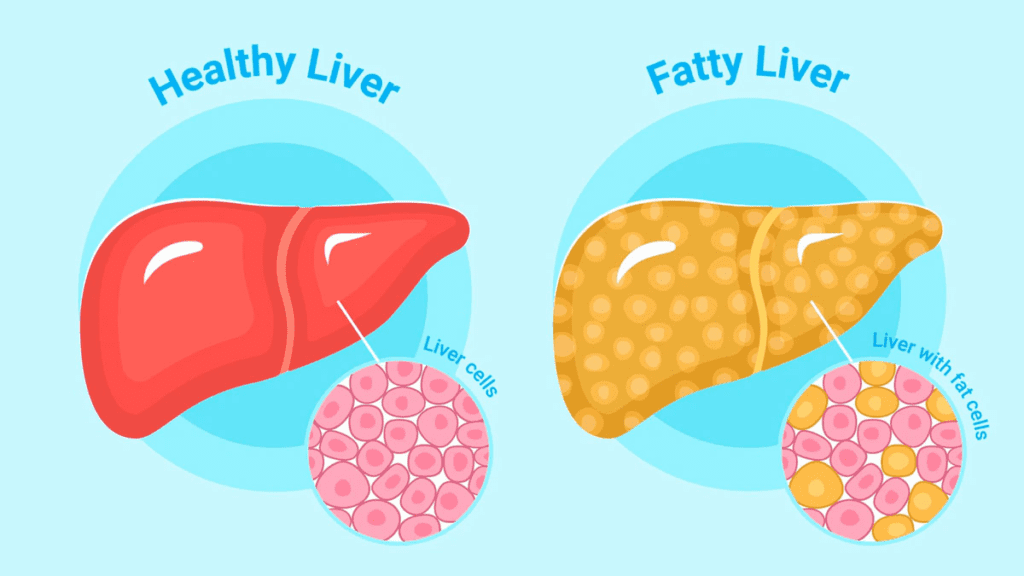
To understand fatty liver disease, it is necessary to understand its main characteristics. This section will break down the two primary types: alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). By exploring the mechanisms behind fat accumulation in liver cells, readers will gain a fundamental understanding of this widespread health problem.
The Culprits Behind Fatty Liver
This section will analyze the various causes and risk factors associated with fatty liver disease. From excessive alcohol consumption and metabolic syndrome to insulin resistance and genetic predisposition, we will highlight the multifaceted nature of these contributing factors, providing a holistic perspective on the genesis of fatty liver.
Unmasking the Silent Epidemic
Fatty liver disease often works in a latent mode, with minimal symptoms in its early stages. This section will explore the subtle signs and symptoms that may serve as danger signals, urging readers to pay attention to their bodies. Early detection is important for effective intervention and disease management.
Diagnostic Insights
Diagnosing fatty liver involves a combination of medical evaluation and diagnostic tools. From blood tests to imaging studies, this section will guide readers through the diagnostic process. Understanding how health care professionals identify and confirm the presence of fatty liver sets the stage for informed decision making.
Lifestyle as a Catalyst for Change
Lifestyle changes are fundamental in managing and even reversing fatty liver disease. This section will highlight the power of dietary change while emphasizing the importance of a nutrient-rich, well-balanced diet. Additionally, we will explore the role of regular physical activity, weight management, and elimination or abstinence from alcohol intake in promoting liver health.
Collaborative Care and Ongoing Research
Collaboration with healthcare providers is the key to effective fatty liver disease management. This section will discuss medical interventions, emerging treatments, and the importance of regular medical follow-up. By staying informed and engaged in ongoing research, individuals can contribute to progress in the field and benefit from evolving treatment options.
Ultimately, this comprehensive guide strives to empower individuals with the knowledge and tools needed to understand and navigate fatty liver disease. By highlighting its complexities, highlighting preventive measures and emphasizing the importance of collaborative health care, readers can begin the journey towards better liver health and overall well-being. Together, we can move toward a future where the impact of fatty liver disease can be reduced through awareness, education, and proactive health management.
Fatty Liver Disease symptoms
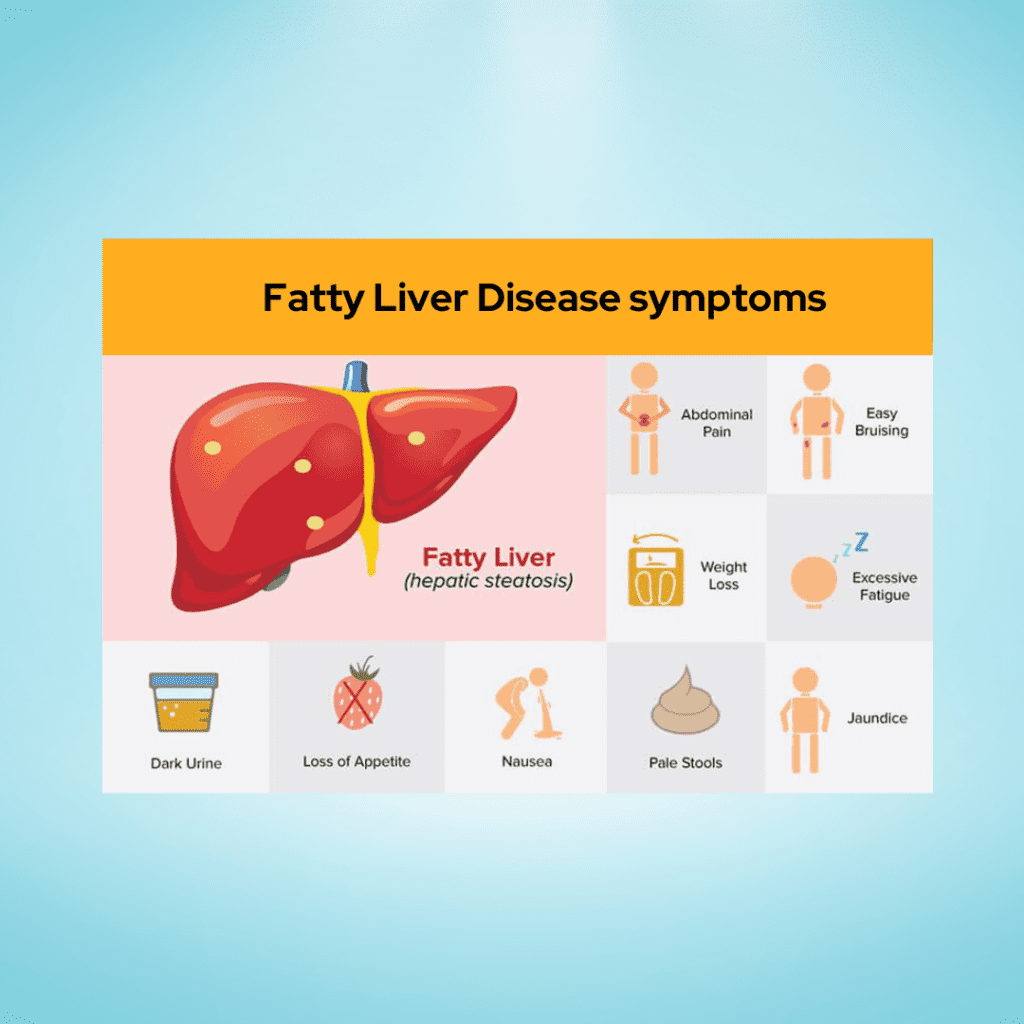
Fatty liver disease is often referred to as a “silent” condition in its early stages because it may not cause noticeable symptoms. However, as the disease progresses, symptoms may begin to manifest. It’s important to note that symptoms can vary in severity and may not be specific to fatty liver disease alone. If you suspect you may have fatty liver disease or are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned below, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management.
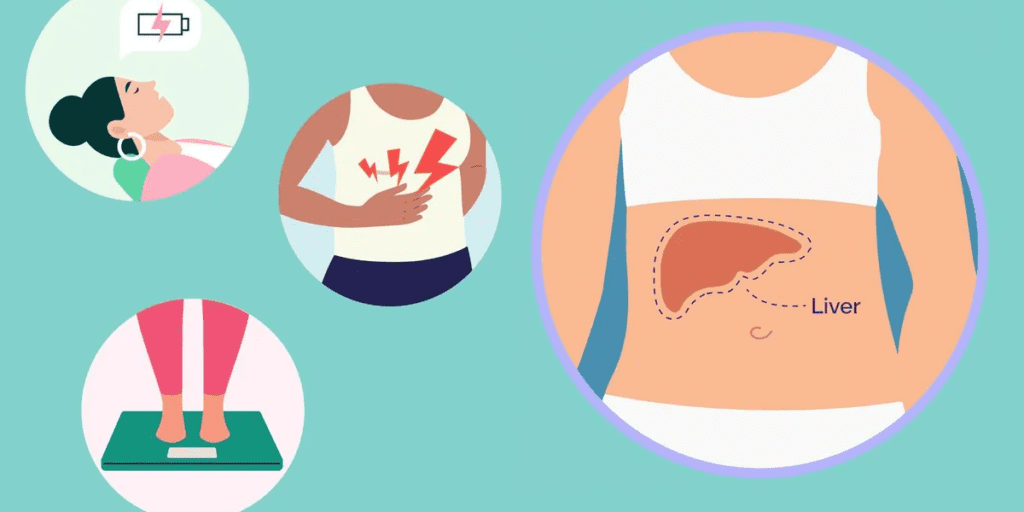
- Fatigue: Generalized fatigue and a feeling of weakness are common symptoms of fatty liver disease. The liver plays a crucial role in energy metabolism, and when it is compromised, it can lead to increased feelings of tiredness.
- Abdominal Discomfort: Some individuals with fatty liver disease may experience discomfort or a dull pain in the upper right side of the abdomen, where the liver is located. This discomfort may be more noticeable after consuming a heavy meal.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Rapid and unexplained weight loss can be a symptom of advanced fatty liver disease. As the liver becomes more impaired, it may affect the body’s ability to process nutrients, leading to unintentional weight loss.
- Enlarged Liver: In some cases, the liver may become enlarged, a condition known as hepatomegaly. This can cause a feeling of fullness or discomfort in the abdominal area.
- Jaundice: Jaundice is a yellowing of the skin and eyes that can occur when the liver is not effectively processing bilirubin. While less common in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, it can be a sign of more advanced liver damage.
- Swelling in the Abdomen and Legs: Fluid retention, known as edema, can occur in individuals with advanced fatty liver disease. This may lead to swelling in the abdomen (ascites) or legs, indicating compromised liver function.
- Confusion and Impaired Mental Function: Severe cases of fatty liver disease may lead to hepatic encephalopathy, a condition characterized by confusion, difficulty concentrating, and impaired mental function. This is a sign of advanced liver dysfunction and requires immediate medical attention.
It’s crucial to remember that not everyone with fatty liver disease will experience symptoms, and the severity of symptoms can vary widely. Regular check-ups, monitoring liver function through blood tests, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are essential for early detection and effective management of fatty liver disease. If you suspect you may have fatty liver disease or are experiencing symptoms, consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
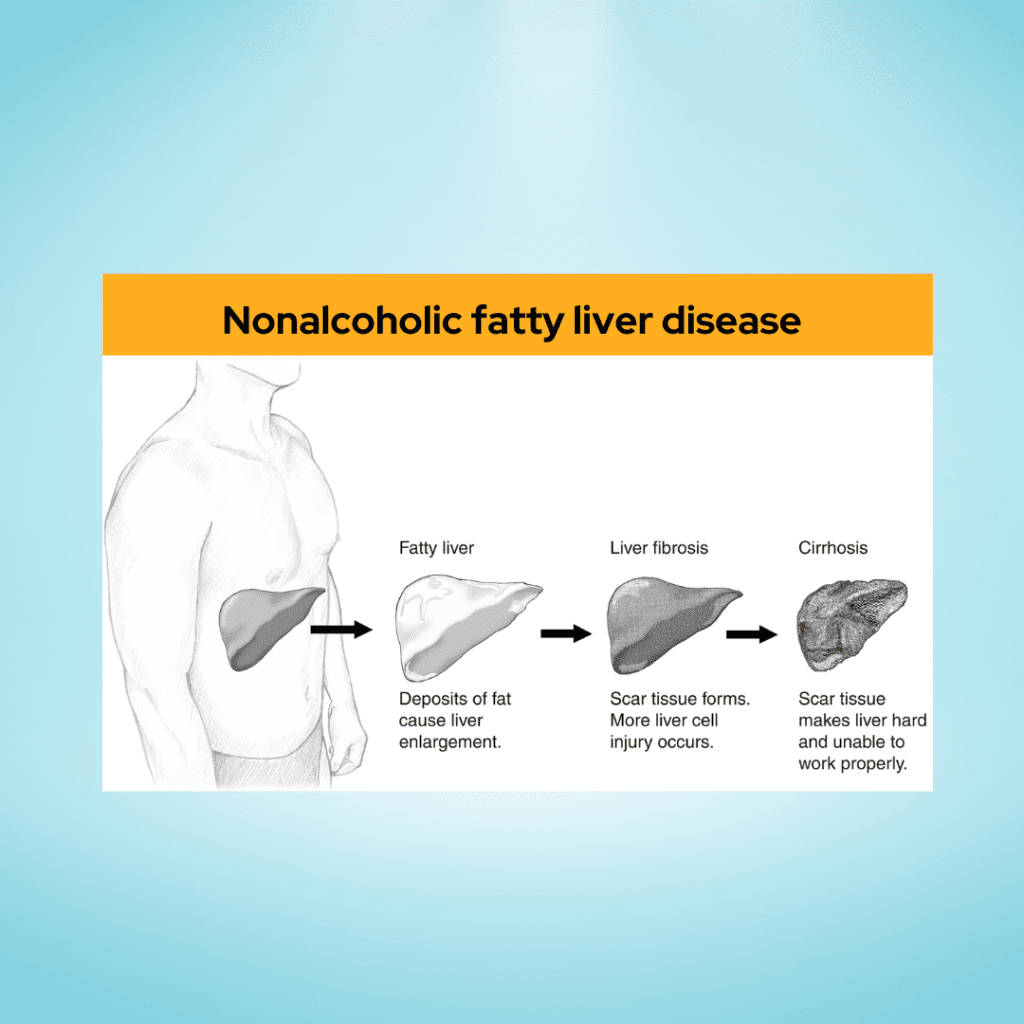
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a prevalent and potentially serious liver condition that is not caused by alcohol consumption. It encompasses a spectrum of liver diseases, ranging from simple fatty liver (steatosis) to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which involves inflammation and liver cell damage. NAFLD is closely associated with obesity, insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and other conditions related to lifestyle and diet. Understanding the key aspects of NAFLD is essential for prevention, early detection, and management.
1. Prevalence and Risk Factors:
NAFLD is becoming increasingly common worldwide, and its prevalence is closely linked to the rising rates of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Other risk factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and metabolic syndrome. Genetic factors and certain medical conditions also contribute to an individual’s susceptibility.
2. Types of NAFLD:
- Simple Fatty Liver (Steatosis): The accumulation of fat in liver cells without inflammation or liver cell damage. It is generally considered a less severe form of NAFLD.
- Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): Involves inflammation and liver cell damage alongside fat accumulation. NASH can progress to more severe liver conditions, including cirrhosis and liver cancer.
3. Symptoms:
- Silent Early Stages: NAFLD is often asymptomatic in its early stages, earning it the label of a “silent” disease.
- Advanced Stages: Symptoms may include fatigue, abdominal discomfort, unexplained weight loss, and, in severe cases, jaundice.
4. Diagnosis:
- Blood Tests: Liver function tests and other blood tests can indicate abnormalities associated with liver health.
- Imaging Studies: Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRIs may be used to detect the presence of fat in the liver and assess its severity.
- Liver Biopsy: In some cases, a liver biopsy may be recommended for a more detailed assessment of liver damage and inflammation.
5. Management and Treatment:
- Lifestyle Changes: The cornerstone of NAFLD management involves adopting a healthy lifestyle. This includes a well-balanced diet, regular physical activity, and weight management.
- Medications: In certain cases, medications may be prescribed to manage specific aspects of NAFLD, such as insulin resistance or high cholesterol.
- Monitoring: Regular monitoring of liver function and associated health markers is crucial to track the progression of the disease.
6. Complications:
- Cirrhosis: Advanced NAFLD can lead to cirrhosis, which is characterized by irreversible scarring of the liver.
- Liver Cancer: Individuals with NASH and cirrhosis have an increased risk of developing liver cancer.
7. Prevention:
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, is key to preventing the development and progression of NAFLD.
- Managing conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and high blood pressure can significantly reduce the risk of NAFLD.
In conclusion, Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease is a complex and multifaceted condition with potentially serious consequences. Early detection, lifestyle changes, and medical management play crucial roles in preventing its progression and improving long-term outcomes. If you suspect you may have NAFLD or are at risk, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
fatty liver disease self-care

Managing fatty liver disease involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and self-care practices. While these strategies are not a substitute for professional medical advice, they can complement medical interventions and contribute to overall liver health. Here are some self-care tips for individuals with fatty liver disease:
1. Adopt a Healthy Diet:
- Balanced Nutrition: Focus on a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit processed foods, saturated fats, and added sugars.
- Portion Control: Practice mindful eating and be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating. Consider consulting with a dietitian for personalized dietary guidance.
2. Weight Management:
- Gradual Weight Loss: If overweight or obese, aim for gradual weight loss through a combination of a healthy diet and regular exercise. Rapid weight loss can sometimes worsen liver function.
3. Regular Physical Activity:
- Aerobic Exercise: Engage in regular aerobic exercises such as walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
- Strength Training: Include strength training exercises to build muscle, which can help improve insulin sensitivity and metabolic health.
4. Limit Alcohol Consumption:
- Abstain or Moderate: If diagnosed with fatty liver disease, it’s advisable to abstain from alcohol. Even moderate alcohol consumption can exacerbate liver damage.
5. Control Blood Sugar and Cholesterol:
- Manage Diabetes: If diabetic, work with healthcare professionals to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
- Control Cholesterol: Keep cholesterol levels in check through dietary modifications, exercise, and medications if prescribed.
6. Hydration:
- Adequate Water Intake: Stay well-hydrated by consuming an adequate amount of water throughout the day. Proper hydration supports overall health and helps the liver function optimally.
7. Avoid Crash Diets:
- Sustainable Approaches: Avoid crash diets or extreme weight-loss measures. Instead, focus on sustainable lifestyle changes that can be maintained in the long term.
8. Monitor and Manage Stress:
- Stress Reduction Techniques: Practice stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or other relaxation techniques.
9. Regular Medical Check-ups:
- Routine Monitoring: Adhere to regular check-ups with healthcare providers to monitor liver function, blood markers, and overall health.
- Medication Adherence: If prescribed medications, take them as directed and discuss any concerns or side effects with your healthcare provider.
10. Educate Yourself:
- Stay Informed: Learn about fatty liver disease, its progression, and how lifestyle changes can positively impact your liver health.
- Ask Questions: Don’t hesitate to ask your healthcare provider questions about your condition, treatment plan, and self-care strategies.
11. Limit Processed Foods and Added Sugars:
- Whole Foods: Choose whole, unprocessed foods and limit the intake of foods high in added sugars. A diet rich in nutrients supports overall health.
Remember, self-care practices are most effective when integrated into a holistic approach to health. It’s crucial to work closely with healthcare professionals to tailor self-care strategies to your specific needs and monitor your progress over time. Always consult with your healthcare provider before making significant changes to your diet, exercise routine, or other aspects of your self-care plan.
Fatty liver disease treatments
The treatment approach for fatty liver disease focuses on lifestyle modifications, addressing underlying risk factors, and managing any existing complications. While there isn’t a specific medication approved solely for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), healthcare providers may recommend various strategies based on the severity of the condition and individual health factors. Here are key components of fatty liver disease treatment:
1. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Dietary Changes: Adopting a balanced, nutrient-dense diet with an emphasis on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limiting saturated fats, added sugars, and processed foods is essential.
- Weight Management: Gradual weight loss, if overweight or obese, is often recommended. Even a modest weight loss can have significant benefits for liver health.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, including both aerobic exercises and strength training, supports overall health and can improve insulin sensitivity.
2. Control of Underlying Conditions:
- Blood Sugar Management: For individuals with diabetes, managing blood sugar levels through medication, diet, and exercise is crucial.
- Cholesterol Control: Keeping cholesterol levels within a healthy range through lifestyle changes and medications if necessary.
3. Avoidance of Alcohol:
- Abstinence or Moderation: Individuals with fatty liver disease, particularly those with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), are often advised to abstain from alcohol or consume it in moderation.
4. Medications:
- Insulin Sensitizers: Medications like pioglitazone may be prescribed to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation in the liver.
- Antioxidants: Vitamin E supplements may be considered for some individuals with NASH, as they have antioxidant properties that can help reduce inflammation.
5. Liver Health Monitoring:
- Regular Check-ups: Routine monitoring of liver function through blood tests and imaging studies can help track the progression of fatty liver disease.
- FibroScan or Liver Biopsy: In some cases, a FibroScan or liver biopsy may be performed to assess the extent of liver damage and fibrosis.
6. Treatment of Complications:
- Management of Cirrhosis: For individuals with advanced liver disease or cirrhosis, management focuses on preventing complications and addressing specific symptoms.
- Liver Cancer Surveillance: Regular monitoring for the development of liver cancer in individuals with advanced liver disease.
7. Weight-Loss Surgery (Bariatric Surgery):
- In some cases of severe obesity and fatty liver disease, weight-loss surgery may be considered. This can result in significant improvements in liver health.
8. Clinical Trials and Research:
- Participation in clinical trials may be an option for some individuals, especially those with advanced disease or those not responding to standard treatments.
It’s important to note that treatment plans are highly individualized, and healthcare providers will consider factors such as the severity of liver disease, the presence of comorbid conditions, and the individual’s overall health. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your treatment plan or starting new medications. The goal of treatment is to prevent progression, manage symptoms, and improve overall liver health.













More Stories
Snokido: The Ultimate Guide to Your Online Gaming Hub
Triumph: The Journey of Kase Abusharkh and Amy Berry
Top 5 Breeds: Best Dogs for Indian Homes